In 1981, two CGIAR member institutes—the International Food Policy Research Institute (IFPRI) and the former International Service for National Agricultural Research (ISNAR)—initiated a joint venture on agricultural research data indicators with the publication of the best available data from secondary sources for an ad hoc group of national agricultural research systems.
In 1984, ISNAR launched its “Indicator Series Project,” carrying out extensive surveys in all developing countries and combining the results with secondary data to produce a fully sourced, 154-country sample of research investment indicators for the period 1961–85. Substantial effort was taken to ensure that the coverage and treatment of these data were consistent over time and among countries.
During 1993–97, ISNAR instigated a second round of data collection to delve below the national aggregate statistics and compile agency-specific data on research expenditures, staffing, research orientation, and so on. At this time, the scope of the survey was broadened to include the agricultural research activities carried out by universities, which markedly improved country comparability.
During 1997–2000, IFPRI and ISNAR jointly instigated a survey round in Latin America and the Caribbean, the scope of which was again broadened to include activities carried out by private firms. Coverage of the private sector, however, remained limited because most private firms are reluctant to provide information on their human and financial resources.
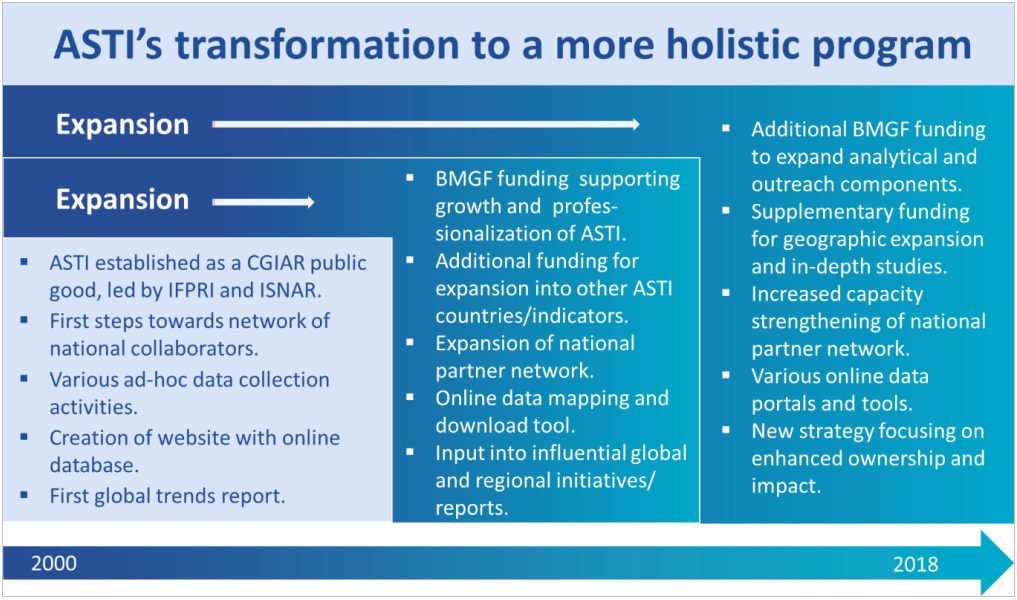
Late in 2000, IFPRI and ISNAR renamed the Indicators Series project the Agricultural Science and Technology Indicators (ASTI) initiative and work continued with funding from the CGIAR. During 2001–08, the initiative focused on developing and maintaining its website; building its network of collaborators; initiating institutional survey rounds in Sub-Saharan Africa, the Asia–Pacific, Latin America and the Caribbean, and the Middle East and North Africa; and writing and producing a set of country briefs and regional synthesis reports quantifying and analyzing major investment and institutional trends.
In 2004, ISNAR ceased operations as an institute, and IFPRI became the sole facilitator of ASTI. In 2008, ASTI received a three-year grant from the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation, and the initiative relocated to Rome. This grant enabled the initiative to update its existing set of science and technology indicators; upgrade its website to enhance performance, broaden the provision of online data and information, foster partnerships with key stakeholders, and the organization of an international conference Agricultural research: Investing in Africa’s future. Analyzing trends, challenges and opportunities.
During 2008—18, ASTI received financial support from the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation (BMGF), with additional generous support from other donors. This funding has enabled ASTI to update its global R&D indicators database, expand and fine-tune its indicators, automate its systems for data collection and reporting, develop interactive data dissemination tools, foster long-term partnerships with stakeholders, expand its analytical activities, and enhance outreach for increased impact.
Since 2018, ASTI has begun the implementation of a new network approach focused on transferring the ownership of the data, analyses, and outreach to regional and country levels, and building a network of technical and policy partners supporting this transition.