The ASTI Data in Focus series provides additional background data in support of the 2010 Country Note on Ghana (asti.cgiar.org/pdf/Ghana-Note.pdf) prepared by the Agricultural Science and Technology Indicators (ASTI) initiative and the Science and Technology Policy Research Institute (STEPRI). Based on data collected by ASTI and STEPRI, these two outputs review major investment and capacity trends in Ghanaian public agricultural research and development (R&D) since 1971, providing important updates on agricultural R&D trends prepared by ASTI and STEPRI in 2003–04.
D. Research Allocation across Commodities and Themes
This section provides detailed quantitative information on Ghanaian public agricultural research allocation for 2008. Complementary sections of this issue on Ghana present detailed data on long-term trends (Section A), financial resources (Section B), and human resources (Section C). Further supporting information provides macroeconomic trends, a list of agencies included in the study, data sources and estimation procedures, and ASTI’s methodology.
Table D1—Research focus by major commodity area, 2008
This table presents researcher numbers by major commodity area both in absolute and relative terms. In 2008, the largest number of researchers (343 FTEs) focused on crops research. Of the remaining researchers, 41 FTEs focused on forestry research, 33 on fisheries research, 37 on livestock research, and 14 on natural resources research. The other 70 researchers concentrated their efforts on socioeconomic research, postharvest research, or other matters.
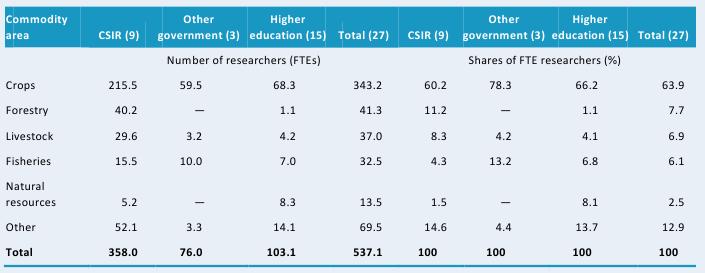
Source: Calculated by authors from IFPRI–STEPRI 2009.
Note: Figures in parentheses indicate the number of agencies in each category.
Figure D1—Research focus by major commodity area, 2008
This figure presents data on the allocation of FTE researchers across commodity areas (see alsoTable D1). In 2008, close to two-thirds of Ghana’s 537 FTE researchers in agriculture were involved in crop research, 8 percent focused on forestry research, 6 percent focused on fisheries research, 7 percent focused on livestock research, and 3 percent focused on natural resources research. The remaining researchers concentrated on socioeconomic, postharvest, or other research.
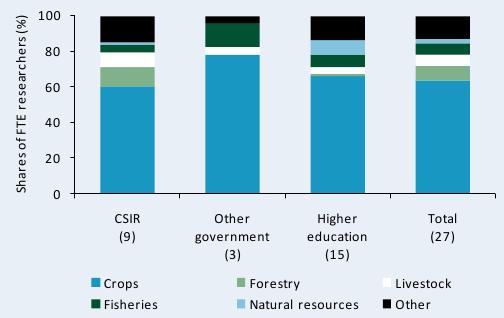
Source: Calculated by authors from IFPRI–STEPRI 2009.
Note: Figures in parentheses indicate the number of agencies in each category.
Table D2—Focus of crop and livestock research by major item, 2008
In 2008, the most researched crop in Ghana—employing 41 FTE researchers and representing 10 percent of total (combined) crop and livestock research, was cassava. Other important crops were cocoa and maize (9 percent each) and rice (8 percent). The country’s livestock researchers primarily concentrated on swine, sheep and goats, and poultry. Agencies under the Council for Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR) conducted research into a variety of commodities. The Food Research Institute (FRI), Crop Research Institute (CRI), Plant Genetic Resources Research Institute (PGRRI) focused on more than 10 different commodities in 2008. Other government agencies focused on their respective mandates. The Animal Research Institute (ARI) under CSIR and the Biotechnology and Nuclear Agricultural Research Institute (BNARI) were the only agencies to conduct livestock research. In 2008, 30 of ARI’s 37 FTE researchers and 3 of BNARI’s 20 FTE researchers focused on livestock research.
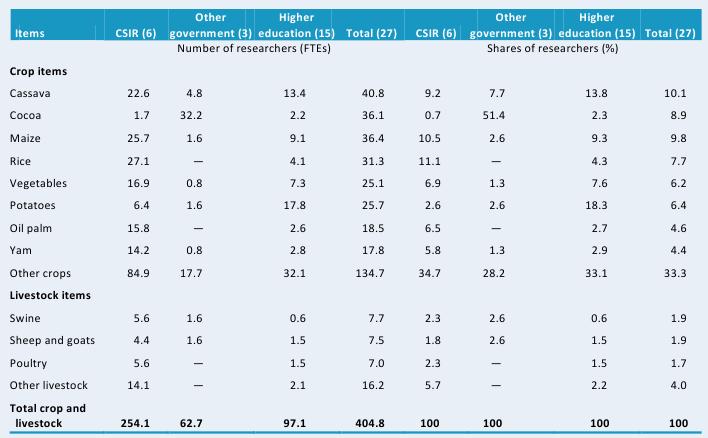
Source: Calculated by authors from IFPRI–STEPRI 2009.
Note: Figures in parentheses indicate the number of agencies in each category.
Table D3—Focus of crop and livestock research by major theme, 2008
This table shows FTE researchers by thematic area in absolute and relative terms. Natural resources are an important research theme in Ghana accounting for 214 of the 487 FTE researchers in 2008. That year, 15 percent of Ghana’s agricultural researchers focused on crop genetic improvement, 10 percent focused on crop pest and disease control, and 19 percent focused on other crop-related research. Natural resource research was another important area, accounting for 16 percent of the country’s agricultural researchers. Large variations were, however, reported across agencies: for example, 21 percent of researchers at agencies under the Council for Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR) focused on natural resources research, whereas few researchers at the other agencies worked in this area.
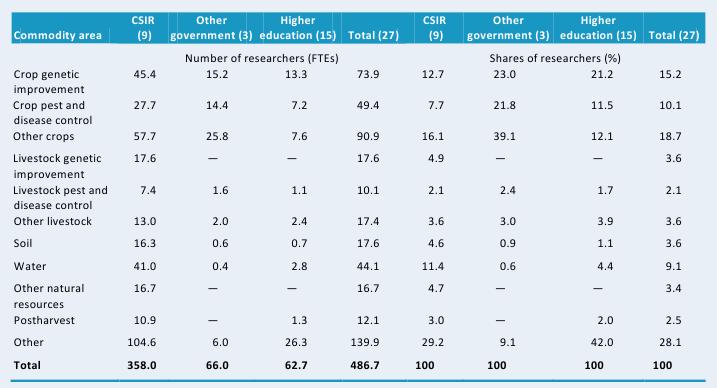
Source: Calculated by authors from IFPRI-STEPRI 2009.
Note: Figures in parentheses indicate the number of agencies in each category.
